
Magic Bibliography: Scholarly and Professional Research into Theatrical Magic

Peter Prevos |
1723 words | 9 minutes
Share this content
Theatrical magic is surrounded by secrecy, and magicians have sworn oaths to each other not to divulge their methods. This veil of secrecy is, however, transparent. Magicians publish books and videos to teach each other. The art of magic has also attracted academics and professionals’ attention in a wide range of fields. Researchers have asked questions of theatrical magic from diverse disciplines, from dentistry and linguistics to management and gender studies.
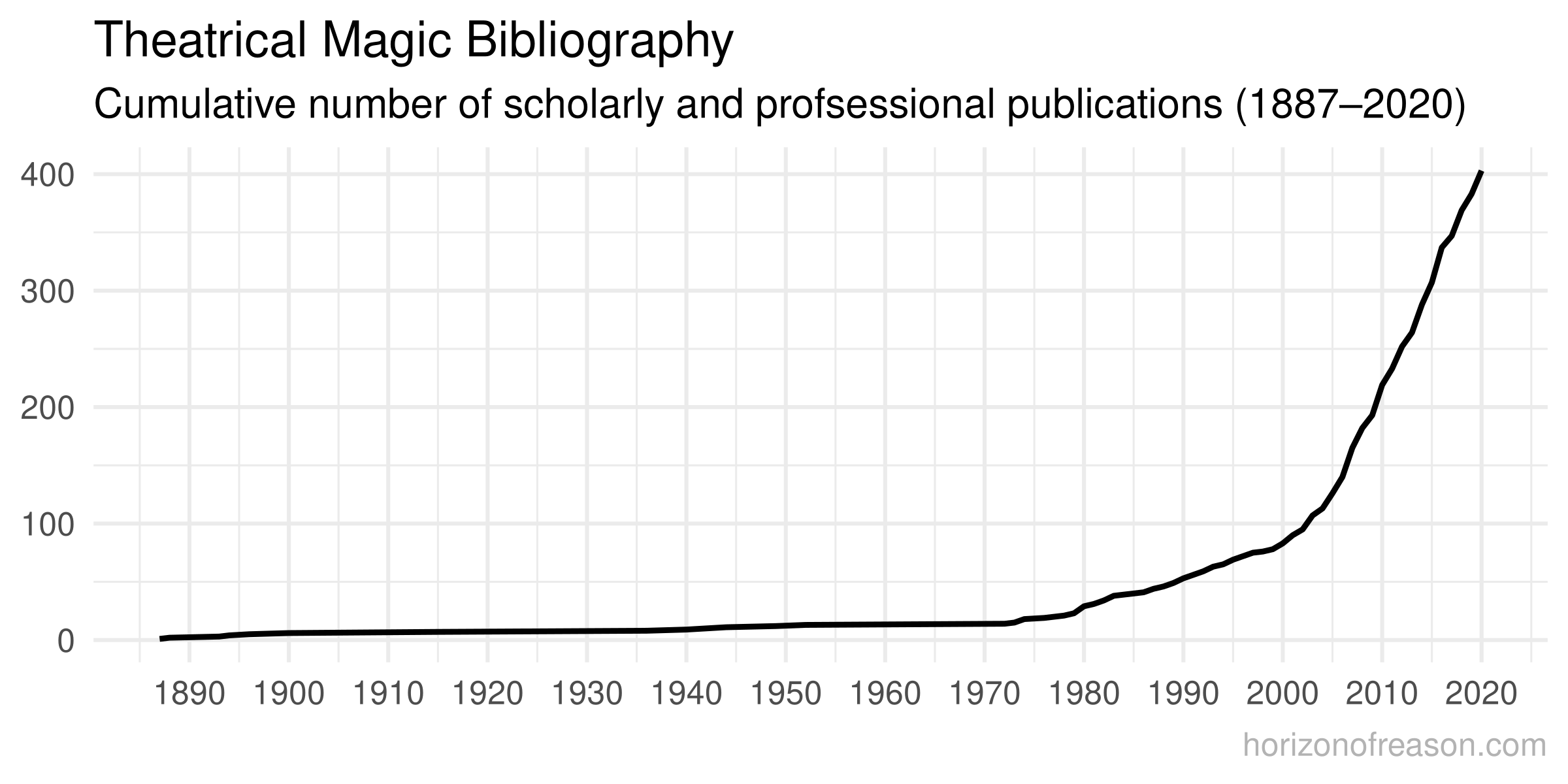
This magic bibliography provides a comprehensive list of No file scholarly and professional articles, conference papers and books on conjuring.
The relationship between science and magic is complex. Scholars from many different fields have studied performance magic. Magicians often use the principles of science to seemingly breaks the laws of nature. Magic and science have a bidirectional relationship where both fields of human endeavour relate to each other
Magic Bibliography Inclusion Criteria
The criteria for inclusion in this magic bibliography are:
- Published in a peer-reviewed academic or professional book, journal or conference proceedings, from any branch of science.
- Discuss any aspect of theatrical magic (conjuring).
- Empirical and conceptual articles
- Use magic tricks (deception) as an experimental method
The following publications are excluded from the bibliography:
- Generic normative discourse on how to perform magic, such as explanations of tricks and rules of performance.
- Book reviews
I am for completeness, so feel free to contact me if there are any mistakes or missing entries in this bibliography.
My book Perspectives on Magic discusses many of the references listed below.
Magic Bibliography Categories
Most of the estimated half a million magicians around the world are amateurs or semi-professionals. They work as lawyers, occupational therapists, psychologists, computer scientists, teachers and so on. Many of these scientists and professionals have written scholarly papers and books about their passion.
The word “science” usually relates to the natural sciences, such as physics. However, the scientific work on conjuring illustrates that science is a much broader concept than the physical sciences alone. The science of magic discusses the full spectrum of human experience and the natural world. There are broadly four branches of science:
- Natural and physical sciences: cosmology, geology, physics, chemistry and biology.
- Formal sciences: mathematics and logic.
- Social sciences: psychology, sociology and the humanities.
- Applied sciences: engineering, medicine and computer science.
To fully understand a complex phenomenon such as theatrical magic, scientists use various perspectives beyond the natural sciences. Scientists and professionals from two of the four domains of science have studied the art of conjuring, each asking their specific questions of magic. The word cloud below visualises the relative frequency of each of the entries in this magic bibliography.

The categorisation of science is not always precise. For example, psychology, the most significant contributor to conjuring science, can be social science and biological science. Psychology often studies the external attributes of behaviour. Still, it more recently is also involved with looking inside the body for a more physical approach. Works in the applied sciences can often be placed into two categories. For example, education and physics or medicine and biology.
Formal Sciences
Mathematics
Many magic tricks are based on the principles of mathematics, which makes them a suitable vehicle for teachers. Some aspects of magic, such as shuffling cards, have been studied in detail by mathematicians.
ERROR
Computer Science
Mathematics and computer sciences are close cousins in the family of science. Papers in this field use magic as a metaphor to explain complex issues.
ERROR
Natural and Physical Sciences
Magic could be defined as that which science has not yet made intelligible. Magicians often use scientific principles to create the illusion of magic. A few centuries ago, magicians often adorned themselves with academic titles. Magic tricks are, as such, an entertaining way to illustrate the principles of physics to students.
ERROR
Social Sciences
The social sciences concern themselves with human behaviour and relationships. Given the wide variety of humanity, the social sciences are very broad with a wide range of methods. From numerical approaches that are akin to the physical sciences, to the more conceptual in philosophy.
Film Studies
Magic and cinema have a lot in common in that they both rely on deception. Magicians, such as Georges Méliès, and Charles Pathé, were the first film exhibitors, performers and producers. Their efforts started the development of special effects as a narrative device. The literature in the genre reviews the role of magicians in the popularisation of cinema and how they responded to its popularity.
ERROR
Gender Studies
Magic is one of the few male-dominated performance arts. Less than five per cent of people actively involved in theatrical magic are women. However, in other performance arts, more than one-third of performers are female. Gender studies explore the possible reasons for the imbalance between men and women in magic as performance art.
ERROR
History
Until recently, social historians had no genuine interest in magic. However, the past decade has seen a steady flow of monographs critically analysing conjuring’s place in society through the ages.
ERROR
Legal Studies
Professional magicians strive for originality to differentiate themselves in the entertainment market. This literature discusses the complex legal issues regarding intellectual property in magic.
ERROR
Library Studies
Magicians are avid collectors of books on how to perform their craft. Some have bequeathed their collections to academic institutions, such as the WG Alma Conjuring Collection in Melbourne, Australia. The articles in this genre of magic literature describe these libraries.
ERROR
Linguistics
Magicians use language to share secrets with each other and use their words wisely to enhance the deception of their audiences. These studies look at how magicians use unique words and drawings to communicate their craft.
ERROR
Performance Studies
Conjuring is a minor form of theatre by the establishment and has only recently been discussed in academic literature. The books and papers analyse the aesthetics of magic as a performance art.
ERROR
Psychology
Psychologists are the most significant contributors to the science of magic. The main question they try to answer is why it is so easy to deceive people. This part of the bibliography largely overlaps with the Science of Magic Bibliography by Matt Tompkins. Tomkins focuses on experimental research with adult participants.
Science of Magic
The literature in this subcategory discusses the nature of the science of magic from the psychologist’s perspective.
ERROR
Perception Psychology
The majority of works in this bibliography study perception psychology. These studies either research magic tricks as a topic or as an experimental methodology to investigate other questions.
ERROR
Parapsychology
The field of parapsychology is one of the most controversial of the sciences. Parapsychologists study the concept of real magic. To ensure the integrity of their experiments, parapsychologists can employ magicians to ensure that subjects don’t use nefarious methods.
ERROR
Sociology and Anthropology
The social sciences look at the social world of magicians—how they are organised, how they share secrets and other aspects of being a magician. Publications about legal studies review issues related to the intellectual property of magic trick methods and presentations.
ERROR
Applied Sciences
The applied sciences, such as engineering and medicine, use the formal, natural and social sciences as foundations to influence reality. The magic literature in the applied sciences describes how magic tricks or the methods of magicians, in general, can improve people’s lives.
Business Studies
The literature on business magic mainly deals with magic as a metaphor to conduct yourself in an organisation. Managers can learn from magicians about compelling presentations, use the principles of developing new magic tricks to understand innovation. There are also business people who use magic in their professional life to enliven presentations or as ice-breakers. Performing magic tricks can also be a tool to explain complex concepts in management. Using magic as an educational tool is a common thread in magic literature. You can read more about business magic on my Lucid Manager website.
ERROR
Software Development and Robotics
Software designers and magicians have in common that they both create virtual realities. Software designers bring their reality alive on computer displays; magicians bring theirs alive on the stage. See the article on computer magic for a discussion of this literature.
ERROR
Education
Teaching children abstract subjects, such as mathematics or physics, can be a difficult task. However, performing magic stimulates students’ curiosity and motivates them to discover the principles of science used to create magic.
A large amount of literature has been published on the topic, categorised within other subjects, such as management, mathematics and physics.
ERROR
Healthcare
Performing magic in healthcare by medical professionals helps clinical outcomes by reducing stress for, mainly young patients. In some instances, patients themselves perform the magic to improve their mental or physical health.
Magicians Scott Tokar and Harrison J. Caroll have published a book with magic tricks for physicians. Side-Fx describes how medical professionals can perform magic tricks with everyday objects around the examining room, such as cotton balls, tongue depressors and rubber gloves.
Medicine
The medical literature not only describes how physicians can use magic to place their young patients at ease. Some literature analyses some specific medical conditions that relate to magicians.
ERROR
Dentistry
Some dentists use magic tricks to put young patients at ease. Performing a magic trick for children reduces the time it takes them to get them to sit in the dreaded chair and improves the quality of their care.
ERROR
Nursing
The use of magic tricks in nursing is mainly related to performing tricks to help children cope with the anxiety of hospitalisation. Clown Doctors perform their craft in many hospitals around the world.
ERROR
Mental Health Care
In mental health care, patients perform magic tricks to enhance their self-esteem. The therapist has been used to assist in diagnosis.
ERROR
Occupational Therapy
Performing magic tricks can help people with physical disabilities to improve their motor skills and self-confidence. Several programmes exist where magicians and occupational therapists work with patients to improve their life.
ERROR
Share this content
